How To Identify The Lidar Vacuum Robot That Is Right For You
нҺҳмқҙм§Җ м •ліҙ
мһ‘м„ұмһҗ Nickolas мһ‘м„ұмқј24-08-09 23:50 мЎ°нҡҢ6нҡҢ лҢ“кёҖ0кұҙкҙҖл Ёл§ҒнҒ¬
ліёл¬ё
LiDAR-Powered Robot Vacuum Cleaner
Lidar-powered robots are able to map out rooms, providing distance measurements that allow them to navigate around furniture and objects. This lets them clean a room more thoroughly than traditional vacuums.
LiDAR utilizes an invisible laser that spins and is highly accurate. It can be used in dim and bright environments.
Gyroscopes
The gyroscope is a result of the magic of a spinning top that can remain in one place. These devices detect angular motion, allowing robots to determine where they are in space.
A gyroscope is made up of tiny mass with an axis of rotation central to it. When an external force of constant magnitude is applied to the mass, it causes precession of the angular speed of the rotation the axis at a constant rate. The rate of motion is proportional to the direction in which the force is applied as well as to the angular position relative to the frame of reference. The gyroscope measures the speed of rotation of the robot through measuring the angular displacement. It then responds with precise movements. This ensures that the robot remains steady and precise, even in changing environments. It also reduces the energy use which is a major factor for autonomous robots that operate on limited power sources.
An accelerometer works in a similar way like a gyroscope however it is smaller and cheaper. Accelerometer sensors are able to measure changes in gravitational speed by using a variety of techniques, including piezoelectricity and hot air bubbles. The output of the sensor is a change to capacitance which can be converted into a voltage signal using electronic circuitry. By measuring this capacitance the sensor can determine the direction and speed of its movement.
Both accelerometers and gyroscopes are utilized in the majority of modern robot vacuums to create digital maps of the space. The robot vacuums can then utilize this information for swift and efficient navigation. They can detect furniture, walls and other objects in real time to help improve navigation and prevent collisions, leading to more thorough cleaning. This technology is also called mapping and is available in upright and Cylinder vacuums.
However, it is possible for some dirt or debris to block the sensors in a lidar robot, which can hinder them from working efficiently. In order to minimize the chance of this happening, it's advisable to keep the sensor clear of clutter or dust and to check the user manual for troubleshooting tips and advice. Cleaning the sensor can cut down on maintenance costs and enhance performance, while also extending its life.
Sensors Optic
The optical sensor converts light rays into an electrical signal, which is then processed by the microcontroller of the sensor to determine if it detects an item. The data is then sent to the user interface as 1's and zero's. As a result, optical sensors are GDPR CPIA and ISO/IEC 27001 compliant and do not keep any personal data.
The sensors are used in vacuum robots to identify objects and obstacles. The light beam is reflected off the surfaces of objects, and is then reflected back into the sensor. This creates an image that helps the robot navigate. Optics sensors are best utilized in brighter environments, but they can also be utilized in dimly lit areas.
The optical bridge sensor is a typical type of optical sensors. The sensor is comprised of four light detectors connected in the form of a bridge to detect small changes in position of the light beam that is emitted from the sensor. The sensor is able to determine the exact location of the sensor by analysing the data from the light detectors. It can then determine the distance between the sensor and the object it is detecting and adjust the distance accordingly.
A line-scan optical sensor is another type of common. This sensor measures distances between the sensor and the surface by analysing the variations in the intensity of the light reflected off the surface. This type of sensor is ideal to determine the height of objects and avoiding collisions.
Some vacuum robots have an integrated line-scan scanner that can be manually activated by the user. This sensor will activate when the robot is set to hitting an object. The user is able to stop the robot using the remote by pressing a button. This feature can be used to shield fragile surfaces like furniture or carpets.
The navigation system of a robot is based on gyroscopes optical sensors, and other parts. They calculate the position and direction of the robot, and also the location of obstacles in the home. This allows the robot to create an accurate map of space and avoid collisions when cleaning. However, these sensors aren't able to produce as precise maps as a vacuum robot that uses LiDAR or camera-based technology.
Wall Sensors
Wall sensors stop your robot from pinging against walls and large furniture. This could cause damage as well as noise. They are particularly useful in Edge Mode where your robot cleans around the edges of the room to remove the debris. They also aid in helping your robot move from one room into another by permitting it to "see" boundaries and walls. These sensors can be used to create no-go zones in your app. This will prevent your robot from vacuuming areas such as wires and cords.
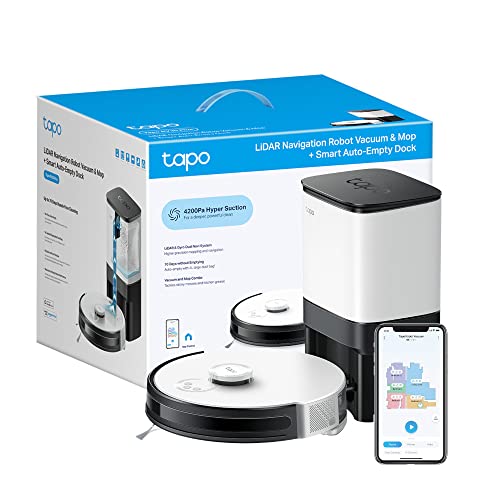

Lidar-powered robots are able to map out rooms, providing distance measurements that allow them to navigate around furniture and objects. This lets them clean a room more thoroughly than traditional vacuums.
LiDAR utilizes an invisible laser that spins and is highly accurate. It can be used in dim and bright environments.
Gyroscopes
The gyroscope is a result of the magic of a spinning top that can remain in one place. These devices detect angular motion, allowing robots to determine where they are in space.
A gyroscope is made up of tiny mass with an axis of rotation central to it. When an external force of constant magnitude is applied to the mass, it causes precession of the angular speed of the rotation the axis at a constant rate. The rate of motion is proportional to the direction in which the force is applied as well as to the angular position relative to the frame of reference. The gyroscope measures the speed of rotation of the robot through measuring the angular displacement. It then responds with precise movements. This ensures that the robot remains steady and precise, even in changing environments. It also reduces the energy use which is a major factor for autonomous robots that operate on limited power sources.
An accelerometer works in a similar way like a gyroscope however it is smaller and cheaper. Accelerometer sensors are able to measure changes in gravitational speed by using a variety of techniques, including piezoelectricity and hot air bubbles. The output of the sensor is a change to capacitance which can be converted into a voltage signal using electronic circuitry. By measuring this capacitance the sensor can determine the direction and speed of its movement.
Both accelerometers and gyroscopes are utilized in the majority of modern robot vacuums to create digital maps of the space. The robot vacuums can then utilize this information for swift and efficient navigation. They can detect furniture, walls and other objects in real time to help improve navigation and prevent collisions, leading to more thorough cleaning. This technology is also called mapping and is available in upright and Cylinder vacuums.
However, it is possible for some dirt or debris to block the sensors in a lidar robot, which can hinder them from working efficiently. In order to minimize the chance of this happening, it's advisable to keep the sensor clear of clutter or dust and to check the user manual for troubleshooting tips and advice. Cleaning the sensor can cut down on maintenance costs and enhance performance, while also extending its life.
Sensors Optic
The optical sensor converts light rays into an electrical signal, which is then processed by the microcontroller of the sensor to determine if it detects an item. The data is then sent to the user interface as 1's and zero's. As a result, optical sensors are GDPR CPIA and ISO/IEC 27001 compliant and do not keep any personal data.
The sensors are used in vacuum robots to identify objects and obstacles. The light beam is reflected off the surfaces of objects, and is then reflected back into the sensor. This creates an image that helps the robot navigate. Optics sensors are best utilized in brighter environments, but they can also be utilized in dimly lit areas.
The optical bridge sensor is a typical type of optical sensors. The sensor is comprised of four light detectors connected in the form of a bridge to detect small changes in position of the light beam that is emitted from the sensor. The sensor is able to determine the exact location of the sensor by analysing the data from the light detectors. It can then determine the distance between the sensor and the object it is detecting and adjust the distance accordingly.
A line-scan optical sensor is another type of common. This sensor measures distances between the sensor and the surface by analysing the variations in the intensity of the light reflected off the surface. This type of sensor is ideal to determine the height of objects and avoiding collisions.
Some vacuum robots have an integrated line-scan scanner that can be manually activated by the user. This sensor will activate when the robot is set to hitting an object. The user is able to stop the robot using the remote by pressing a button. This feature can be used to shield fragile surfaces like furniture or carpets.
The navigation system of a robot is based on gyroscopes optical sensors, and other parts. They calculate the position and direction of the robot, and also the location of obstacles in the home. This allows the robot to create an accurate map of space and avoid collisions when cleaning. However, these sensors aren't able to produce as precise maps as a vacuum robot that uses LiDAR or camera-based technology.
Wall Sensors
Wall sensors stop your robot from pinging against walls and large furniture. This could cause damage as well as noise. They are particularly useful in Edge Mode where your robot cleans around the edges of the room to remove the debris. They also aid in helping your robot move from one room into another by permitting it to "see" boundaries and walls. These sensors can be used to create no-go zones in your app. This will prevent your robot from vacuuming areas such as wires and cords.

лҢ“кёҖлӘ©лЎқ
л“ұлЎқлҗң лҢ“кёҖмқҙ м—ҶмҠөлӢҲлӢӨ.